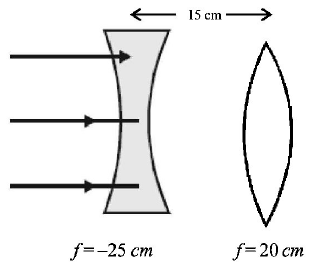
1. A convex lens and a concave lens, each having same focal length of $$25\,cm,$$ are put in contact to form a combination of lenses. The power in diopters of the combination is
A.
25
B.
50
C.
infinite
D.
zero
Answer :
zero
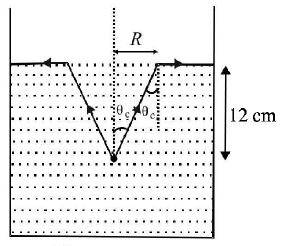
2. A fish looking up through the water sees the outside world contained in a circular horizon. If the refractive index of water is $$\frac{4}{3}$$ and the fish is $$12\,cm$$ below the surface, the radius of this circle in $$cm$$ is
A.
$$\frac{{36}}{{\sqrt 7 }}$$
B.
$$36\sqrt 7 $$
C.
$$4\sqrt 5 $$
D.
$$36\sqrt 5 $$
Answer :
$$\frac{{36}}{{\sqrt 7 }}$$
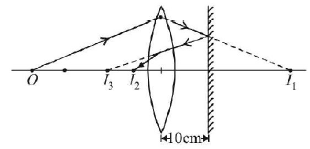
3. A diverging lens with magnitude of focal length $$25\,cm$$ is placed at a distance of $$15\,cm$$ from a converging lens of magnitude of focal length $$20\,cm.$$ A beam of parallel light falls on the diverging lens. The final image formed is:
A.
real and at a distance of $$40\,cm$$ from the divergent lens
B.
real and at a distance of $$6\,cm$$ from the convergent lens
C.
real and at a distance of $$40\,cm$$ from convergent lens
D.
virtual and at a distance of $$40\,cm$$ from convergent lens.
Answer :
real and at a distance of $$40\,cm$$ from convergent lens
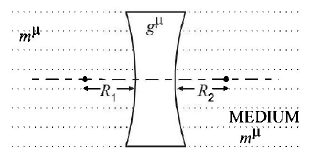
4. A plano convex lens fits exactly into a plano concave lens. Their plane surface are parallel to each other. If the lenses are made of different materials of refractive indices $${\mu _1}\,\& \,{\mu _2}$$ and $$R$$ is the radius of curvature of the curved surface of the lenses, then focal length of combination is
A.
$$\frac{R}{{{\mu _1} - {\mu _2}}}$$
B.
$$\frac{{2R}}{{{\mu _1} - {\mu _2}}}$$
C.
$$\frac{R}{{2\left( {{\mu _1} - {\mu _2}} \right)}}$$
D.
$$\frac{R}{{2 - \left( {{\mu _1} + {\mu _2}} \right)}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{R}{{{\mu _1} - {\mu _2}}}$$
5. Focal length of a convex lens will be maximum for
A.
blue light
B.
yellow light
C.
green light
D.
red light
Answer :
red light
6. A biconvex lens of focal length $$15\,cm$$ is in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the lens and the mirror is $$10\,cm.$$ A small object is kept at a distance of $$30\,cm$$ from the lens. The final image is
A.
virtual and at a distance of $$16\,cm$$ from the mirror
B.
real and at a distance of $$16\,cm$$ from the mirror
C.
virtual and at a distance of $$20\,cm$$ from the mirror
D.
real and at a distance of $$20\,cm$$ from the mirror
Answer :
real and at a distance of $$16\,cm$$ from the mirror
7. A thin glass (refractive index 1.5) lens has optical power of $$- 5\,D$$ in air. Its optical power in a liquid medium with refractive index 1.6 will be
A.
$$- 1\,D$$
B.
$$1\,D$$
C.
$$- 25\,D$$
D.
$$25\,D$$
Answer :
$$1\,D$$
8. A telescope has an objective lens of $$10\,cm$$ diameter and is situated at a distance of one kilometre from two objects. The minimum distance between these two objects, which can be resolved by the telescope, when the mean wavelength of light is $$5000\,\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^ \circ ,$$ is of the order of
A.
$$0.5\,cm$$
B.
$$5\,m$$
C.
$$5\,mm$$
D.
$$5\,cm$$
Answer :
$$5\,mm$$
9. A concave lens of glass, refractive index 1.5 has both surfaces of same radius of curvature $$R.$$ On immersion in a medium of refractive index 1.75, it will behave as a
A.
convergent lens of focal length 3.5 $$R$$
B.
convergent lens of focal length 3.0 $$R$$
C.
divergent lens of focal length 3.5 $$R$$
D.
divergent lens of focal length 3.0 $$R$$
Answer :
convergent lens of focal length 3.5 $$R$$
10. The graph between angle of deviation $$\left( \delta \right)$$ and angle of incidence $$(i)$$ for a triangular prism is represented by
A.
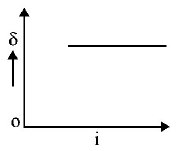

B.
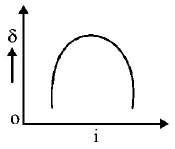

C.
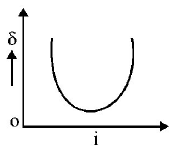

D.
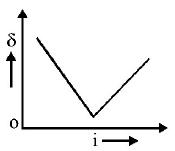

Answer :