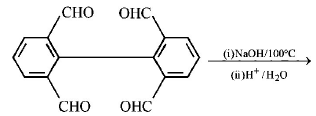
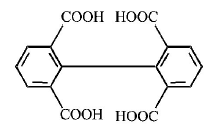
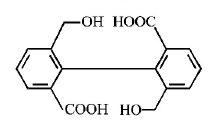
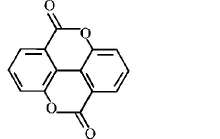
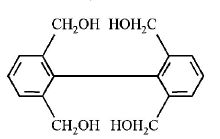
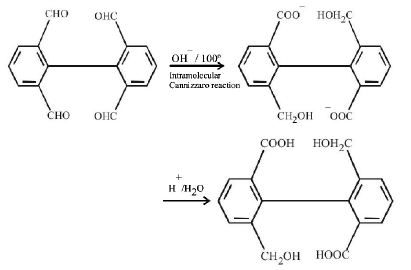
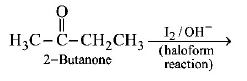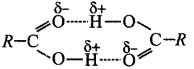1. How will you convert butan - 2 - one to propanoic acid?
A.
Tollen’s reagent
B.
Fehling’s solution
C.
$$NaOH/{I_2}/{H^ + }$$
D.
$$NaOH/Na/{H^ + }$$
Answer :
$$NaOH/{I_2}/{H^ + }$$
2.
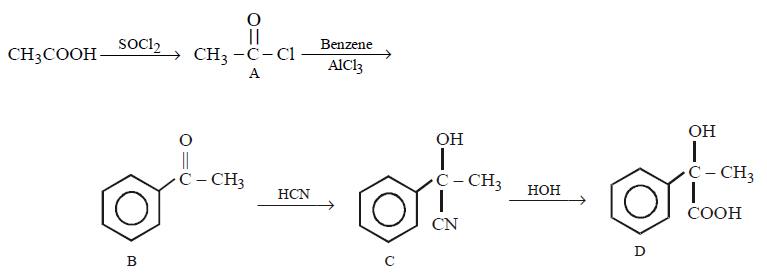
In a set of reactions, acetic acid yielded a product $$D.$$
\[C{{H}_{3}}COOH\xrightarrow{SOC{{l}_{2}}}\left( A \right)\xrightarrow[AlC{{l}_{3}}]{\text{Benzene}}\left( B \right)\xrightarrow{HCN}\left( C \right)\xrightarrow{HOH}\left( D \right)\]
The structure of $$(D)$$ would be –
A.
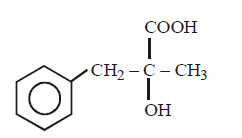

B.
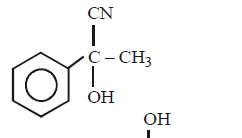

C.
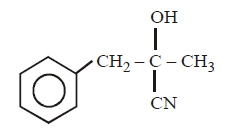

D.
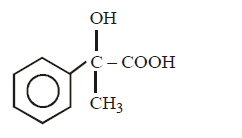

Answer :


3. Carboxylic acids dimerise due to
A.
high molecular weight
B.
coordinate bonding
C.
intermolecular hydrogen bonding
D.
covalent bonding
Answer :
intermolecular hydrogen bonding
4. Among the following the strongest acid is
A.
$$C{H_3}COOH$$
B.
$$C{H_2}ClC{H_2}COOH$$
C.
$$C{H_2}ClCOOH$$
D.
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}COOH$$
Answer :
$$C{H_2}ClCOOH$$
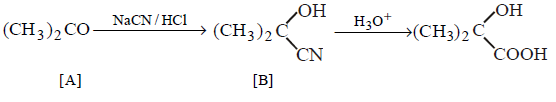
5.
\[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CO\xrightarrow[\left( HCl \right)]{NaCN}A\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}}B\]
In the above sequence of reactions $$A$$ and $$B$$ are
A.
\[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)CN,{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)COOH\]
B.
\[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)CN,{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\]
C.
\[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)CN,{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHCOOH\]
D.
\[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)CN,{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C=O\]
Answer :
\[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)CN,{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)COOH\]
6. The compound that undergoes decarboxylation most readily under mild condition is
A.
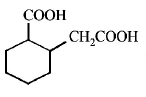

B.
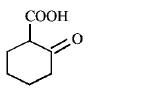

C.
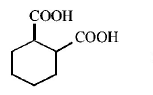

D.
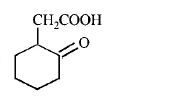

Answer :


7.
Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.

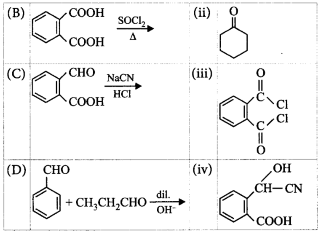
A.
A- i, B - ii, C - iii, D - iv
B.
A - iii, B - iv, C - i, D - ii
C.
A - iv, B - i, C - ii, D - iii
D.
A - ii, B - iii, C - iv, D - i
Answer :
A - ii, B - iii, C - iv, D - i
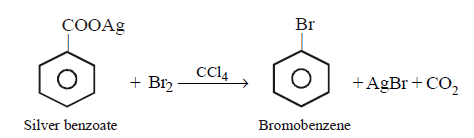
9. Silver benzoate will react with bromine in \[CC{{l}_{4}}\] to form :
A.
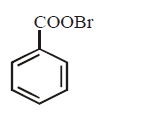

B.
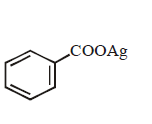

C.
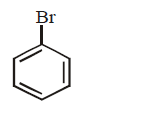

D.
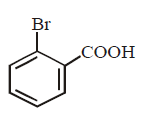

Answer :


10. The most reactive compound towards formation of cyanohydrin on treatment with $$KCN$$ followed by acidification is
A.
benzaldehyde
B.
$$p$$ - nitrobenzaldehyde
C.
phenylacetaldehyde
D.
$$p$$ - hydroxybenzaldehyde
Answer :
$$p$$ - nitrobenzaldehyde